onTrak Accuracy
Agricision offer two levels of accuracy with the onTrak systems, which you will find detailed on the onTrak page and comparison information for individual onTrak accuracy.
The information below is intended to inform our customers the differences between the accuracy expectations.
Both the onTrak original and onTrak ion use signals from multiple satellites at the same time.
The onTrak original and the onTrak ion utilise all freely available satellite signals to obtain the best possible accuracy out the box with no additional cost. Given that the satellite signals are provided free of charge by national governments it is not possible for Agricision to guarantee the onTrak accuracy achieved by onTrak devices not utilising veriTrak.
Due to the improved hardware in the onTrak ion the out of the box accuracy is generally expected to be better, but the results vary with time, location and atmospheric conditions.

Position is important for onTrak accuracy
The onTrak device must be fitted in such a position that it has an unimpeded view of the sky. On a tractor we recommend positioning right on the very tip of the bonnet to ensure the cab is not restricting the view of the sky
On other vehicles an effort should be made to keep the onTrak away for objects that will interfere with the signal such as cabs & exhausts. Positioning onTrak inside the cab would greatly reduce onTrak accuracy.
Out of the box onTrak accuracy (free)
This is an estimate of pass to pass accuracy achievable by an onTrak device out of the box using only freely available satellite signals. Due to random errors in the freely available signals and atmospheric considerations, all figures are estimates only and can’t be guaranteed.
The original onTrak contains a high quality, multi-constellation GNSS receiver with an active antenna and low pass filtering. In essence the hardware used in the system is very good quality given the relatively low price point of the system.
The onTrak ion contains a more advanced GNSS receiver, with a multiband receiver and the ability to decode and utilise the veriTrak correctional data if available.
Main satellite providers used by onTrak systems:
- GPS, owned by the United States Government with 32 operational satellites and worldwide coverage
- GLONASS, owned by the Russian Government with 24 operational satellites and worldwide coverage
- Galileo, created by the European Union with 23 operational satellites and worldwide coverage
- BeiDou, owned by the China National Space Administration with 25 operational satellites and worldwide coverage with focus on Asia and Pacific regions
Regional specific correction services used by all onTrak systems:
- QSZZ, developed by the Japanese, works helps to improve the accuracy of onTraks operating in Japan and Oceania
- EGNOS, developed by the European Space Agency, helps to improve accuracy of onTraks operating in Europe & North Africa
- WAAS, developed by The Federal Aviation Administration, helps to improve the accuracy of onTraks operating in the USA & Canada.
onTrak accuracy using veriTrak (Paid)
This is a firm expectation of the absolute accuracy achieved by onTrak ion devices using Agricision’s veriTrak correction services.
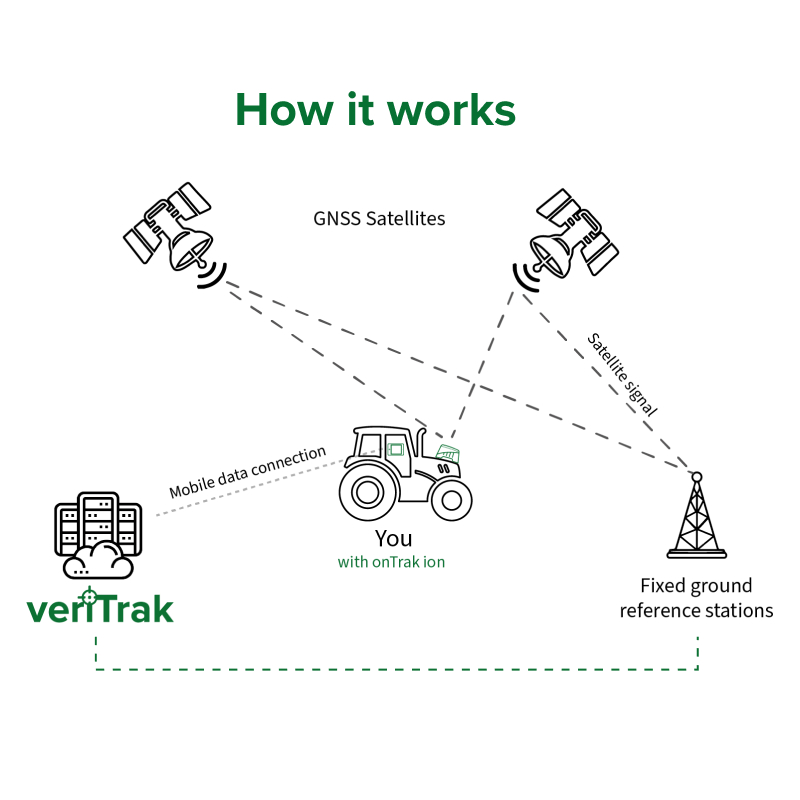
veriTrak is a paid correction service for onTrak ion devices which combines fixed ground station positioning data to increase the accuracy of normal satellite data. Agricison purchase correctional data from their partners around the world and due to the commercial nature of the service Agricision are able to reliably ensure the higher levels of accuracy.
The pass to pass and absolute accuracy when using veriTrak should be approximately the same.
Definition
Absolute accuracy
This is the error of the location coordinates determined by onTrak compared to the actual coordinates of location. This measure is only really important when wishing to return to precisely the same point in a field year on year or accurately surveying a feature.
Definition
Pass to Pass accuracy
This is the average observed error between two consecutive passes across a field. For example if the desired pass spacing (implement width) was 10 meters and the driver followed the onTrak guidance perfectly accurately and the resulting pass spacing was 10.3 meters then the error and hence pass to pass accuracy would be 0.3 meters.

Agricision’s correction service delivered over mobile data for even greater precision farming and improving onTrak ion accuracy. veriTrak uses GPS correction data delivered in realtime to your mobile or data tablet.
